A. LAN (Local Area Network) Design
LAN Overview
A hierarchical network style model, as critical a flat network style model, creates a additional a lot of purposeful
network by differentiating network devices into core, distribution, and access layers, that creates a hierarchy of
network devices and offers the network the subsequent benefits:
• scalability – is improved as a result of having distribution layer three switches segments the network, creates
multiple broadcast domains, and distributes routing duties, this successively permits the flexibility to feature a lot
of access layer switches and add a lot of host computers.
• Redundancy – rather than having only 1 solution of the network, a hierarchical network style creates
redundant, interconnected (meshed) distribution layer and core layer switches permitting a lot of methods for
traffic to flow.
• manageability – centralized management computer code will manage from the distribution layer
• increased bandwidth resources – larger network segmentation can cause higher bandwidth availableness
• increased Security – having over one distribution layer switch permits differentiated security policies and
network security services.
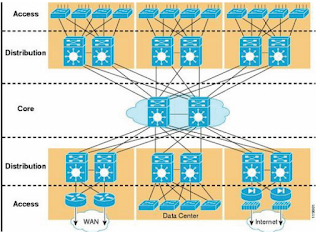
Network Design Model
Access Layer -This layer is used to attach finish devices to the network like PC’s, IP phones, and Printers. This
layer can also embody switches and routers particularly workgroup switches that hook up with finish users. The
Access Layer is additionally wont to enable and management that devices will communicate on the network.
Fixed Switch
Module Switch
Distribution Layer -This is that the layer wherever we tend to apply filtering and apply network policies. The
distribution layer controls the flow of the network, adds redundancy, and adds routing functions between VLANs.
High performance switches.
Core Layer – The core is that the backbone of the network and it needs the best level of information measure,
usually fiber optic connections. The core connects to the ISP and has major routers and switches with
redundancy. The core interconnects the distribution layer switches and routers.
Switch Attributes
Port Security – the flexibility to assemble that host mac addresses may be on a port, and conclusion ports if
they’re not the required host raincoat addresses.
PoE (power over ethernet) – the flexibility to use bound ethernet wire pairs for wattage rather than information.
Link Aggregation – the flexibility to possess multiple ports work along as transmission ports, effectively doubling
and multiplication transmission speeds.
QoS (quality of service)– the flexibility to tell apart and place bound kinds of traffic like voice information.
Port Density – what percentage ports a switch has.
VLANs (virtual local area networks) – the flexibility to make VLANs and assign ports to separate VLANs
Access List control – Layer three practicality. A layer three switch, that may be a switch and a router combined
is required.
Switch types
Fixed Configuration Switches -Cannot be modified or altered, port density is ready.
Modular Switches – may be altered by adding switch blade
ports.
Stackable Switches – Special high speed backplane for
connecting the switches along.
Switching Modes
Store and Forward – Slowest, most reliable
Cut Through switching – quicker, however less reliable
Fast Forward – quickest, least reliable. The switch forwards
the packet/frame once it’s stripped off the destination mac
address.
Fragment Free – Second quickest. The switch forwards
the packet when reading the primary sixty four bytes.



EmoticonEmoticon